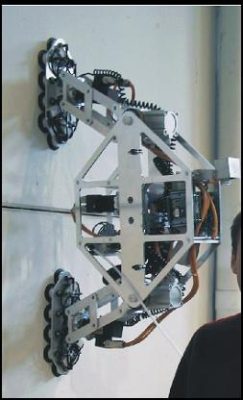
For complex climbing robots, which work in difficult 3D outdoor environments, the gravity force has an important influence with respect the robots changes during its motion. This type of climbing robots is self-supported in the complex 3D structures (bridges, skeleton of the buildings, etc.) which require periodic, manually performed inspections and maintenance. The use of non-conventional climbing robots for this type of operation is highly appropriate. Their locomotion system commonly comprises arms/legs that permit the robot’s 3D mobility (gait). These mechanisms also enable the robot to support itself and guarantee its stability.
The RoboticsLab research in the field of climbing robots starts in 1995. Since this date several robots had been developed: a) Roma 1 was developed for inspection steel-based structures, like steel-beams based infrastructures like bridges, skeletons of the buildings, etc. Its grasping mechanism is able to securely grasp beams and columns, b) Roma 2 for travel along concrete, wood or plastic surfaces, by using a suction cups mechanism; its weight was substantially reduced by using several developed design criteria, and c) Mats robot allows moving in domestic interior environment.by using specially located docking stations. Being the robots? mobility different in some aspects, it was demonstrated that climbing in a complex 3D environment is possible with a high level of security.