Introduction
Many research areas exist in Robotics, for example, the developement of robotic arms, manipulator robots, humanoids and robots created for disable people´s assistance.
A common caracteristic between all those robots is the need of a manipulator which allows it to fulfil certain tasks. This manipulator should be universal in order to give the robot the possibility of being used in as many tasks as the user may want or need. For that reason, the objetive of imitating the human hand grows: it is the best manipulator created by Nature.
Currently, The Robotic´s Lab has two projects:
- RL1 Hand
- UC3M Hand
RL1 Hand
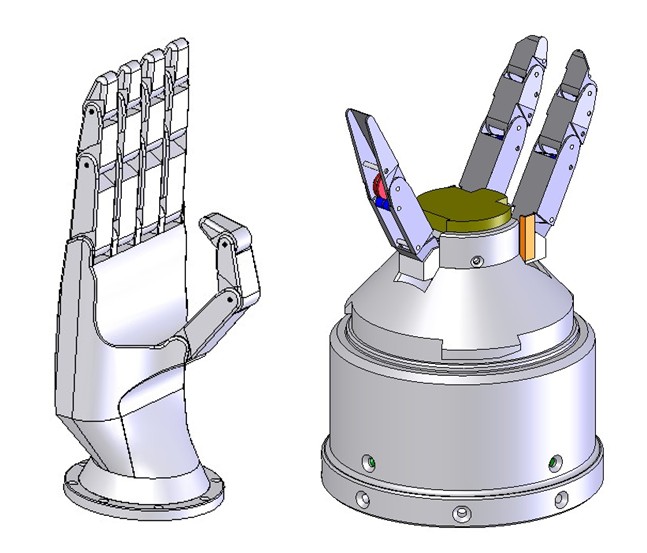
The RL1 Hand is a Robotic Claw design to be mounted on the ASIBOT Robot for helping disable people. Due to the fact that the claw was expected to fit inside the Robot´s Docking Station it had to reach certain caracteristics. A Docking Station is a mechanism that allows the robot to trasnsport throught different enviroments; this feature makes the ASIBOT Robot a climbing robot.


The movement to make the claw pass from a resting state (inside the Docking Station) to a operative state, requires a high complexity internal mechanism. This movement is achieved by only one electrical motor, situated inside the Docking Station with the electronic that controls the claw.

The RL1 Hand´s fingers are able to adapt to the objects shape; this guarantee a firm holding in all cases. The three finger are activated by tendons guide throght pulleys.
The RL1 Hand recives specific instructions given by the ASIBOT Robot, throght the serial port.
Nowadays, a second version of the RL1 Hand is being developed (RL2 Hand), focusing on certain mechanisms optimizations which are expected to make the hand more robust.
UC3M Hand
This project is focused on the development of robotic hand capable of being mounted on the RH0 Humanoid. For that reason, the robotic hand needs to fulfil certain requirements, such us:

- Modular configuration
- Low weight (less than 700 gr.)
- High dexterity
To achieve those requirements, certain objetives have been fixed:
- All the movements must be governed by only one electrical motor
- The UC3M Hand must contain all the mechanism and the electrical motor
- The Humanoid must send simple instruccions to the UC3M Hand to control all its tasks
The objetives mentioned above will be reached by the design of an specific actuator and special mechanisms with a complex coontrol.