In contrast to industrial robots a humanoid robot will interact with a person in the same workspace. To be able to interact with a human and to operate in like a human mode, sensorimotor skills of the robot are required. The humanoid robot must be equipped with actuators and with a number of different sensors to control its movements and monitor its state and to avoid collisions with humans or objects in the environment.
Summarizing the requirements there are:
? hardware architecture must comply with needed computing power
? scalability
? modularity
? standardized interfaces
Especially in humanoid robots there are additional requirements like:
? energy efficiency
? small outline
? lightweight
? small effort in cabling
The main goal of the humanoid robot control system is provide it with stable walking and avoid fallings down. To do this we generate motion pat-terns for each articulation according to the ZMP (Zero Moment Point) theory. The humanoid robot do not falls down when the target ZMP is inside of the support polygon made by the supporting leg(s).
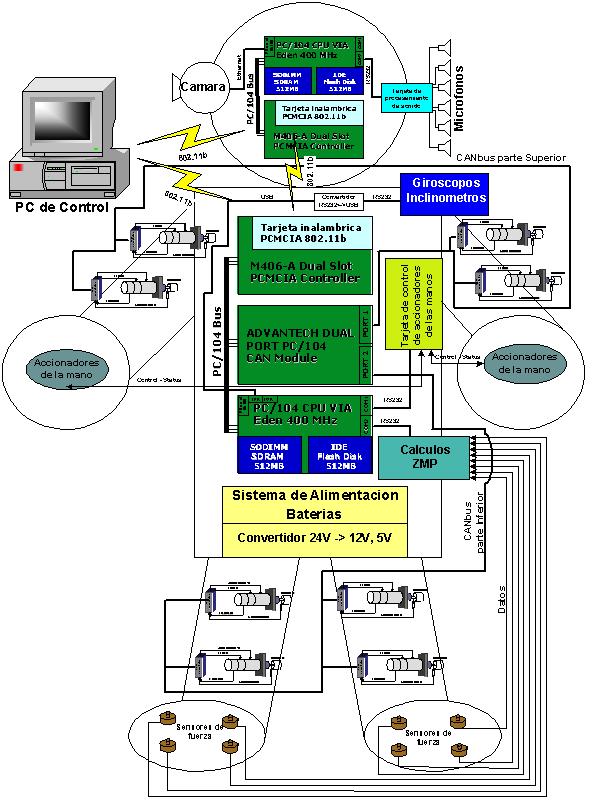
Hardware architecture
Figure 1 shows an overview of the hardware structure. Presented architecture is provided with large level of scalability and modularity by dividing the hardware system into three basic layers. Each layer is represented as a controller centered on its own task such as external communications, motion controller?s network supervision, and general control.

Bottom level software architecture
We developed the bottom level software for the advanced motion control system. It configures intelligent motion controllers, establishes CAN communication, controls trajectory execution and collects motion data which is used in humanoid robot control process. Figure 2 shows the bottom level software architecture.