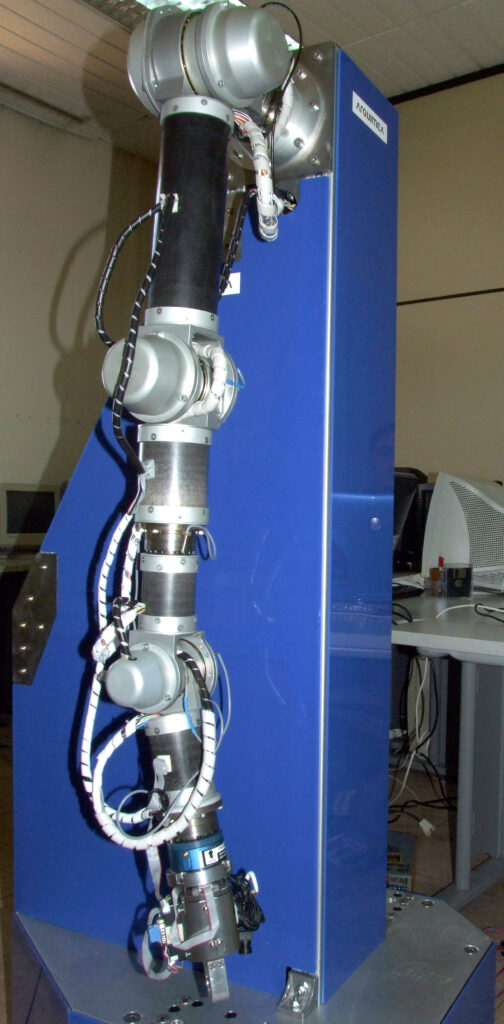
The Light Weight Robot UC3M-1 (LWR-UC3M-1) is a robotic arm with 6 degrees of freedom that allows the robot to do manipulation tasks in human environments. Its main features are the following:
- Kinematic chain similar to the human one.
- Total weight of 18 kilograms.
- Maximum load capability of 4.5 kilograms at the end effector.
- Maximum distance reached around 955 millimeters.
The low-level control of the arm is done with a PMAC PCI control target which allows simultaneous control of 8 motors. Besides, different high level kinematic control techniques have been developed in order to generate the required trajectories for multiple tasks. Among these techniques, the most important ones are:
- Cartesian control based on the analytical Jacobian matrix, which gives us the relationship between the cartesian velocities at the end effector and the required velocities in the articulations in order to execute the required trajectory. This control scheme is based on the one proposed by Sciavicco y Siciliano in “Modelling and control of robot manipulators”, 2005.
- Cartesian control based on the the calculation of the inverse kinematics of the manipulator using evolutionary algorithms. In this case, the Differential Evolution algorithm is used to calculate the motors positions that allow the end effector to reach the desired cartesian point in the space.