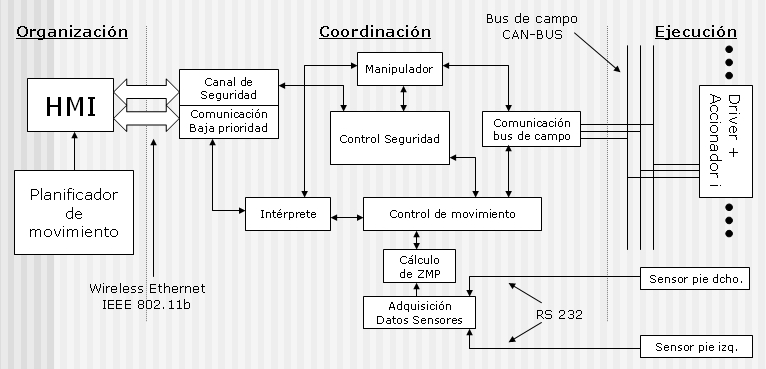
The architecture on development for the RH series of humanoid robots, follows a three layered model: Organization, Coordination & Execution.
The first covers the high level functionality like the HMI, the trajectory generation, the pilot (in a mobile robot fashion), etc.
The second one, Coordination, basically translate the high level commands into drivers commands. Also, must coordinate the movement of the 21 joints and manage the robot state.
The last layer cover the software need to manage a field bus use to comunicate all joint drivers with the central unit.
The fuctionalities aforementioned are what the software team is developing nowadays. In a middle term, the software odn development should fulfill more complex features, like a pseudo-ZMP feedback, a sensorized head and more complex high-level tasks.
The final objective of this development is to bring a modular, scalable, real-time and easy-to-use platform for the development of humanoid skills, human-humanoid interactions and service competences.