Robotics is considered one of the disruptive technologies that will change the lives of citizens in the coming decades. In fact, the largst scientific congress of robotics IEEE / RSJ IROS’2018, which will be held in October in Madrid and is organized by members of this consortium, has the motto “Towards a robotic society”.
Considering also the EU guidelines on the creation of Digital Innovation Hubs, the euRobotics’ MAR and being aligned with the RIS3 strategy of the Community of Madrid, the main objective of the RoboCity2030 program Madrid Robotics Digital Innovation Hub, is the creation in the Community of Madrid of the Ecosystem of robotics and related technologies.
The program, S2018/NMT-4331, funded by “Programas de Actividades I+D en la Comunidad de Madrid” and cofunded by Structural Funds of the EU, consists of six objectives that will allow the development of a sustainable Ecosystem in which all the actors (researchers, companies, society) will promote the creation of a robotic network of added value. The first four objectives oriented to Science and Technology of Excellence are based on the priorities (PAA) of the recently approved HORIZON2020 Work Program of the EU (20182020).
Following these guidelines, the first Objective focuses on Robotics for Health. The aim is to investigate medical and surgical robotics, robotic rehabilitation systems and assistance to people with special needs. The second objective will focus on Robotics Maintenance and Inspection of civil infrastructure (roads, bridges, tunnels) using in each case different types of robots (UAVs, mobile manipulators, AUV and multirobots). The third objective Robotics for Agriculture and Food that will focus on the control of crops, with both terrestrial and aerial robots, and the massive introduction of robots in the food sector. Finally, the fourth objective is Robotics for SMEs through low cost collaborative industrial robot solutions and agile production.
Research will focus, among other topics, on humanrobot interaction, advanced perception, fusion of multisensory systems, learning and cognitive systems, safe movement planning, cooperation and collaboration, robotic cybersecurity.
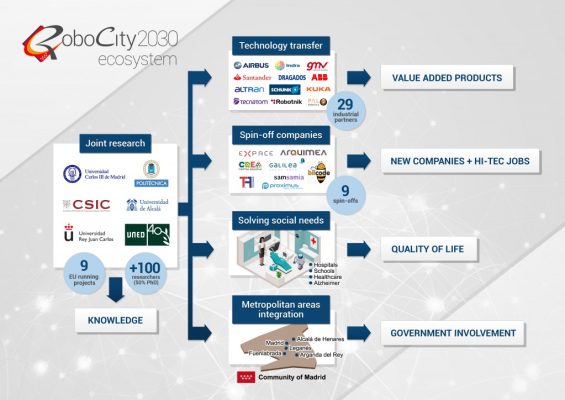
The objective of creating the Ecosystem is divided in three parts: 1) Transfer of technology and business training to boost the universitybusiness relationship, boost collaboration with the HISPAROB technology platform, organize training courses and develop a catalog of services; 2) Development of platforms and infrastructures to be used by researchers and SMEs in proof of concept; 3) Support to Entrepreneurship through the coordination of incubators of robotic companies and scientific advice to entrepreneurial ideas; and 4) Cooperation with other regions (both national and European) for the exchange of experience, attraction and retention of talent and internationalization.
The sixth objective is the dissemination of research results both through scientific publications and generalist activities to raise awareness among administrations, citizens and employers about the benefits of robotics and related technologies.
The RoboCity2030 consortium represents the strongest robotics groups not only in the Community of Madrid and in Spain, but also at European level. Its members have a great prestige and they lead European projects and technological platforms, they are in Committees and International Boards, and they have an important presence in the Science and Technology system of the Community of Madrid. RoboCity2030 also intends to use the FSTP mechanisms to obtain additional funding from other sources such as the Autonomous, State and European, to expand and improve their activities.