This is coordinated project with two university partners. The first partner is Carlos III University of Madrid (UC3M) that has an extensive experience in robotics and artificial intelligence. The second partner is the Technical University of Cartagena (UPCT) that participates trough a new lab directed by a junior researcher, Dr. Oscar Martinez Mozos, from the “Ramon y Cajal Program”. This researcher has a broad international experience in artificial intelligence and assistive robotics.
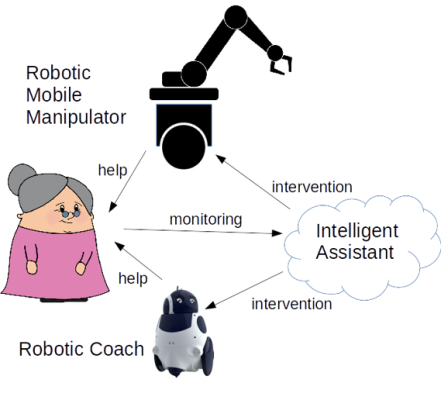
The project presents a heterogeneous robotic platform that supports elderly people during their daily life activities. A system based on distributed artificial intelligence is responsible for the coordination and communication of two robotic platforms that provide physical and mental assistance respectively.
On the one hand, this project presents a robotic assistance platform to support kitchen activities, including cooking. This system requires expertise on robotic manipulation, object detection, planning, control, navigation and grasping amongst others, that will be provided by the RoboticsLab at Carlos III University of Madrid (UC3M). On the other hand, a robotic-based mental coaching system monitors the emotional state of people and suggests activities to improve their mood. This system requires expertise ambient assisted living, sensor data analysis, and machine learning, which is provided by the Ambient Intelligence Lab (AIL) at the Technical University of Cartagena (UPCT). Finally, there is an additional distributed artificial intelligent system that coordinates the previous two subsystems, and that will be jointly deployed by both partners.
The physics assistive robot (UC3M) will be a Mobile Manipulator. It will provides physical assistance for cooking tasks. For de development of this robot, some advances to the state of the art related to path planning, scene recognition and grasping are proposed. The main idea is to take into account 2D-3D information in modeling, path planning and grasping to get optimal paths and grasping task.
In the coaching robot (UCPT), the activities of the daily life of the users will be monitored by non-invasive domestic sensors and personal wearables sensors, and the collected data will be processed by new intelligent algorithms using context information to create a model of the user’s mental health. The assistant robot will use this model and the context to perform personalized coaching in a pro-active way to preserve good mental health and improve the quality of life of the user.
Each robotic subsystem will be tested by the corresponding partner in a set of local demonstrators. In addition, both partners will test the communication and intelligent coordination of both subsystems through internet, which will allow a full joint test where each subsystem is run locally. The final demonstrator will include both subsystems in the same physical arena, that will be deployed at UC3M and consist of as a demonstrator of the Integration of the full system containing both psychical and mental assistive robots a test consist of mental robot detects the end user has hungry and the physical assistance robot prepared food mixing foods in a thermo-mix.
This project provides a positive vision on active and healthy ageing contributing to future dynamic and sustainable health and care systems.